Today’s automotive industry is going full-force into the electric space. But it wasn’t too long ago that automakers were just testing the waters.
Experiments in battery technology, early limited releases and compliance cars led to interesting electric vehicles (EVs) with limited range.
Here’s a rundown of 15 electric car forefathers that paved the way for the Ford Mustang Mach-Es, Volkswagen ID.4s, Subaru Solterras and Toyota BZ4Xs of today.
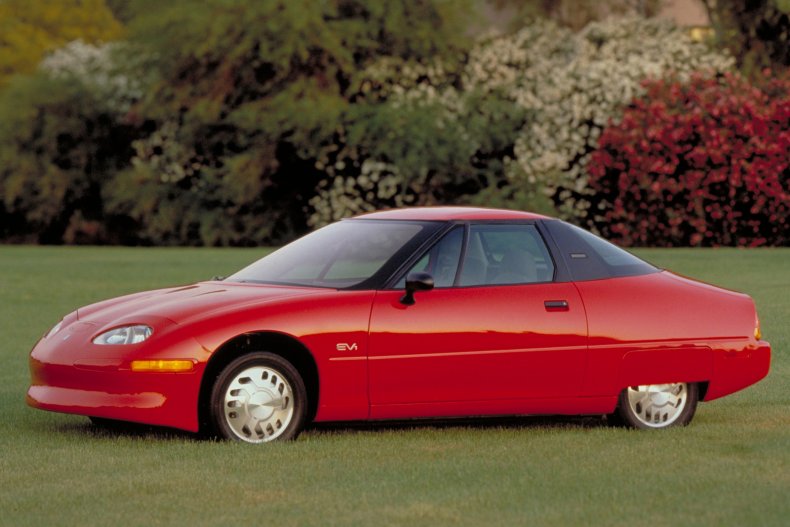
General Motors EV1

General Motors
The EV1 was the first all-electric production car. Between 1996 and 1996, 1,117 models were built and leased to drivers in California, Arizona and Georgia through Saturn dealerships.
An induction AC motor and a 16.5 kilowatt-hour battery pack netted a driver 137 horsepower and 110 pound-feet of torque. The EPA-tested range was about 60 to 80 miles on a single charge.
After the lease terms expired, GM confiscated the cars and scrapped most of them.
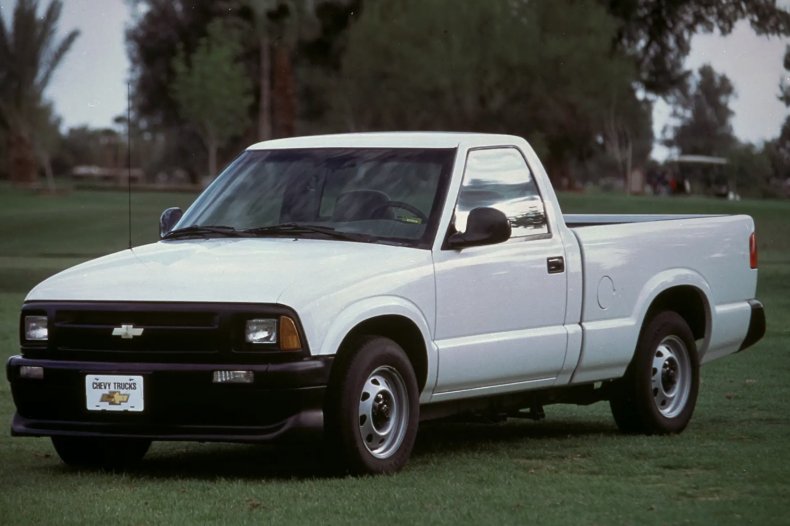
Chevrolet S-10 EV

General Motors
Released in 1996, the electric variant of the S-10 pickup truck was on the market for two years. Sold primarily to fleets, the S-10 was powered by a 85-kilowatt three-phase, liquid-cooled induction motor that was capable of 114 horsepower.
Using a lead-acid battery, the S-10 got an estimated 45.5 miles of range in city driving and 60 miles on the highway.
Of the less than 500 S-10 EVs built, only 60 were sold to fleet customers.
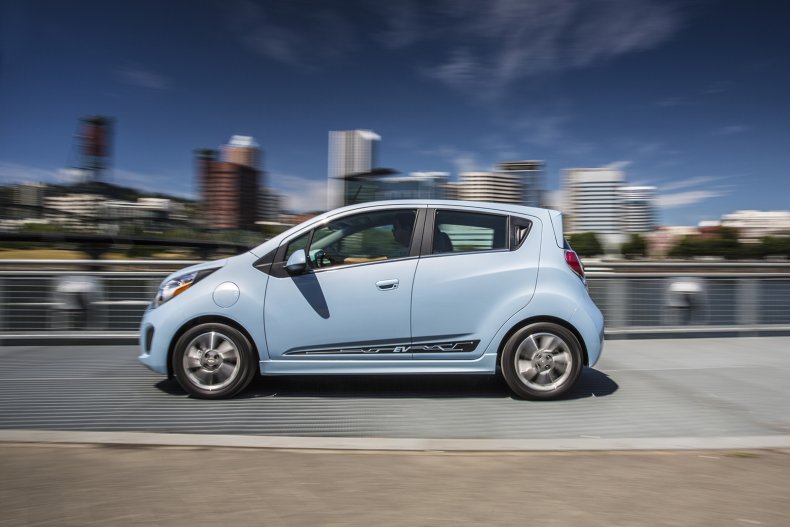
Chevrolet Spark EV

General Motors
Between 2013 and 2016, Chevrolet produced a limited run of EV variants of the Spark, a five-door hatchback. The Spark EV was the first all-electric passenger car marketed by GM since the EV1.
A lithium-ion phosphate battery supplied 82 miles of EPA-estimated range. The EV variant was discontinued in 2016, giving way to the Chevrolet Bolt EV.
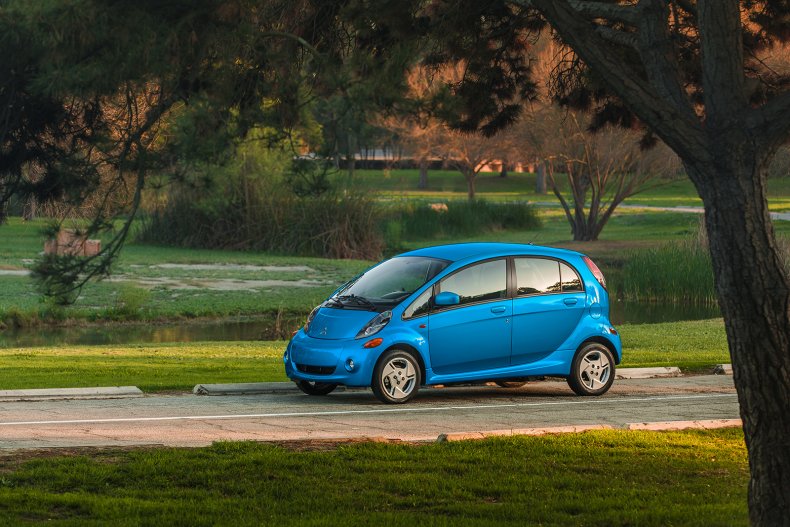
Mitsubishi i-MiEV

Mitsubishi Motors
The Japanese automaker brought the kei-car inspired i-MiEV to the United States for the 2012 model year, selling it for five years (skipping 2015). In its last year of availability in the country, the 2017 i-MiEV was rated for 59 miles on a single charge.
The 2017 model was outfitted with a 49 kilowatt electric motor and a 16 kilowatt-hour lithium-ion battery, which produced 66 horsepower and 145 pound-feet of torque. Retailing for $22,995 before incentives, the i-MiEV was one of the cheapest electric cars on the market during its run.
Ford Ranger EV
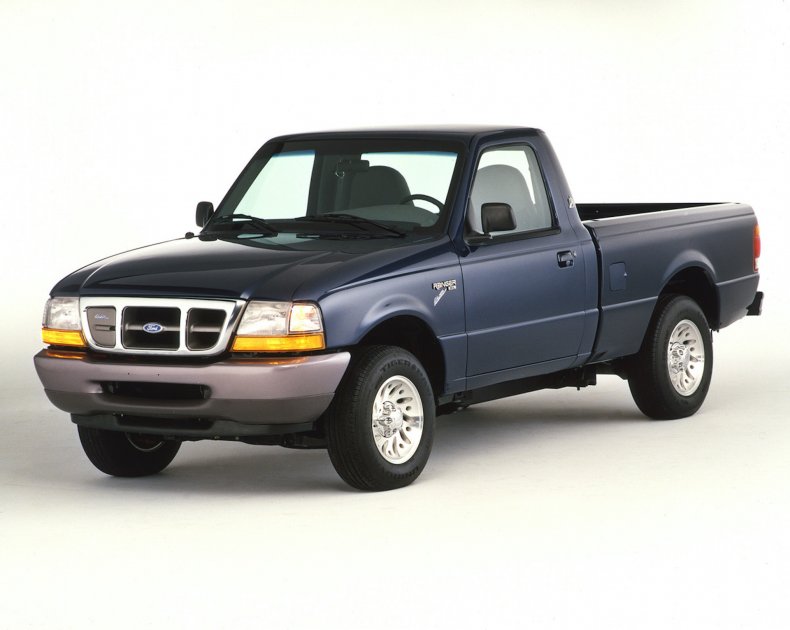

Ford Motor Company
As its first EV, Ford produced the electric version of the compact pickup from 1998 to 2002. Only a few vehicles were sold while most of them were available for lease. Depending on the area, the truck was either powered by a lead-acid battery pack or a nickel-metal hydride variety.
The remaining leases were terminated after 2004 and the trucks were recalled.
Ford Focus Electric
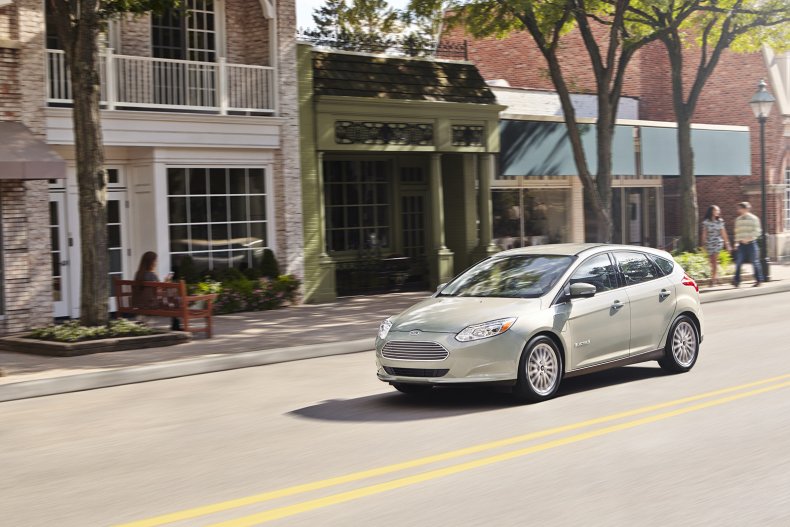

Ford Motor Company
The all-electric Focus was the second EV that Ford produced after the Ranger. Running from 2011 to 2018, Ford sold over 9,000 units in the U.S.
For the 2017 model year, the Focus had an EPA estimated range of 115 miles. That year, the car was powered by a 33.5 kilowatt-hour lithium-ion battery.
BMW i3
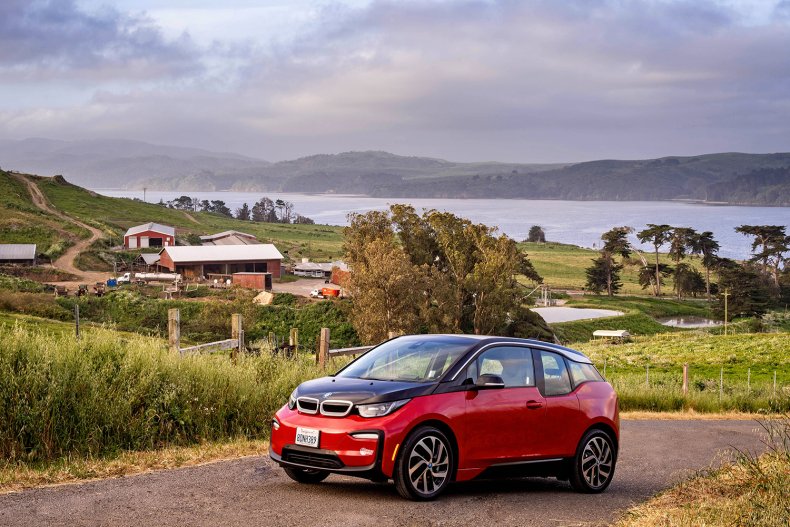

BMW of America, LLC
Announced to the world in 2011, the BMW hatchback was the company’s first mass-produced electric car.
For 2021, the most recent model is rated for 153 miles of range with a 42.2 kilowatt-hour battery. Throughout its run, customers could get the i3 with an inline two-cylinder gasoline-powered range extender.
In June 2021, BMW announced that it would discontinue the i3 in the United States.
Mercedes-Benz B-Class Electric Drive
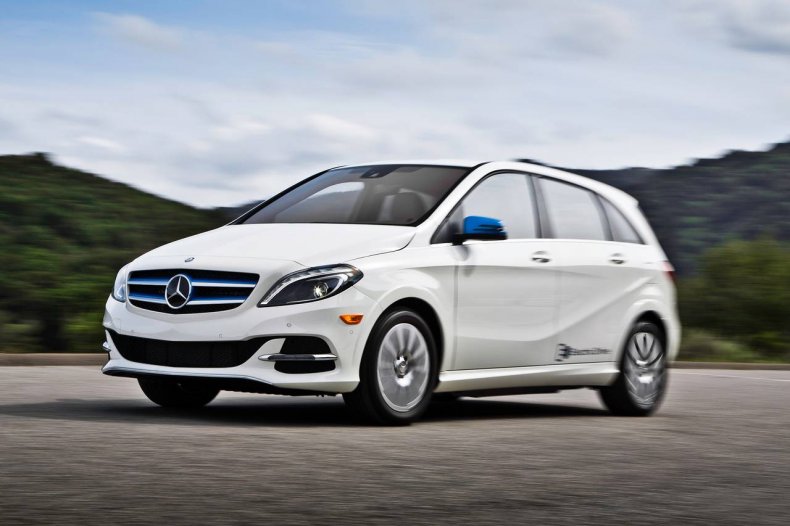

Mercedes-Benz USA
Carrying a B250e designation and built off of the BlueZERO concept car, the German automaker’s subcompact multi-purpose vehicle was on the market from 2014 to 2017. A 36 kilowatt-hour battery built by Tesla put out 134 horsepower and 229 pound-feet of torque. The vehicle could go up to 84 miles on a single charge.
The company announced its discontinuation of the B250e in 2017 as it prioritized the EQ line of electric vehicles.
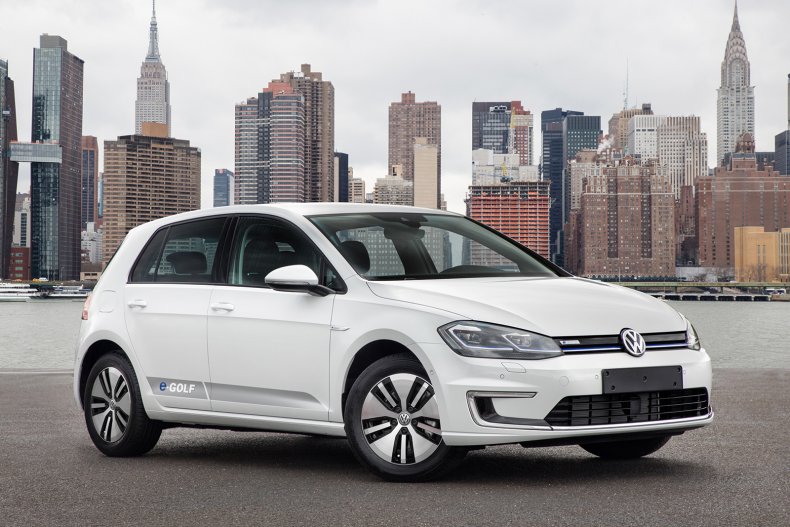
Volkswagen e-Golf

Volkswagen AG
First hitting the European market then making its way to the U.S. towards the end of 2014, the all-electric variant of Volkswagen’s compact car was produced until 2020.
For the 2019 model, the motor gave 125 miles of range and was capable of 134 horsepower.
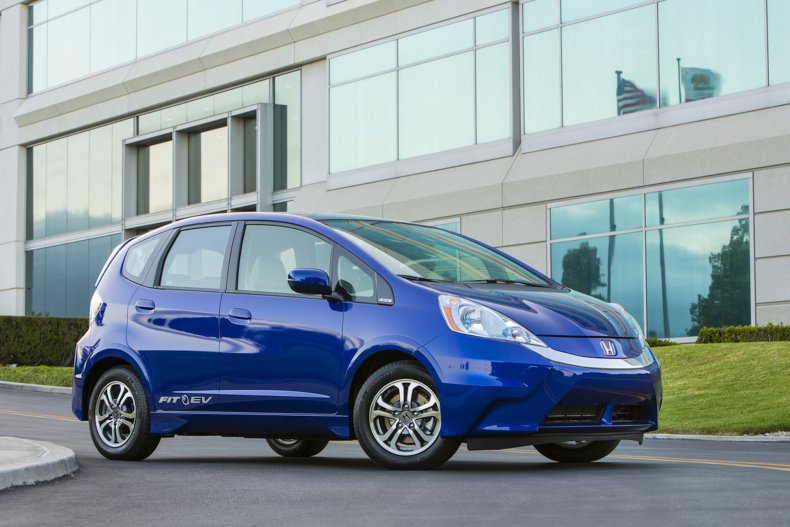
Honda Fit EV

American Honda Motor Co., Inc.
After showing the electric Fit as a concept car at the 2010 Los Angeles Auto Show, the company produced a limited run of the subcompact from 2013 to 2015. Honda only produced 1,100 units.
In its first year of production, the lithium-ion battery gave the Fit a range of 82 miles.
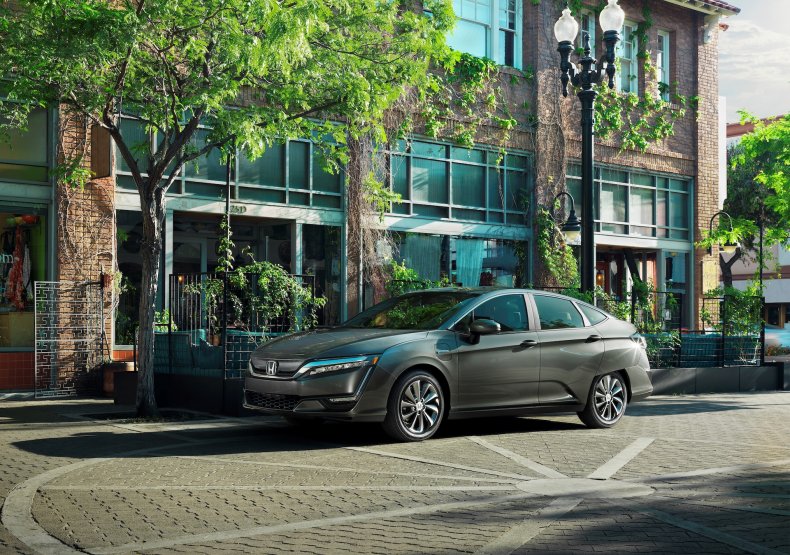
Honda Clarity EV

American Honda Motor Co., Inc.
Under the umbrella of its alternative fuels nameplate, the all-electric version of the Clarity took its place next to the fuel cell and plug-in hybrid models in 2017. A 25.5 kilowatt-hour battery netted the car 89 miles of electric range.
Losing out on range to the competition, Honda phased out the EV model while keeping the other two variants in 2019.
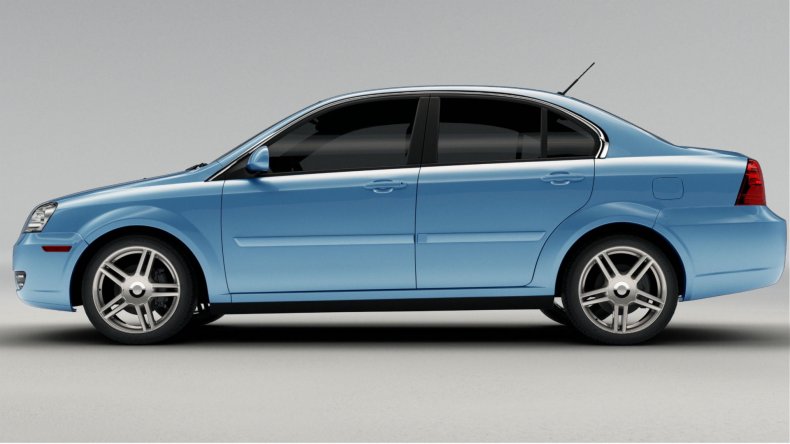
Coda EV

Coda
Coming from a startup that existed from 2009 to 2016, Coda began making deliveries of the Coda all-electric sedan in 2012. The car was adapted from an existing Saibao III body from Chinese manufacturer Hafei.
The car was built with a 31 kilowatt-hour lithium-ion iron phosphate battery that gave a range of 88 miles on a single charge. The company sold 117 units in California.
The company filed for bankruptcy in 2013.
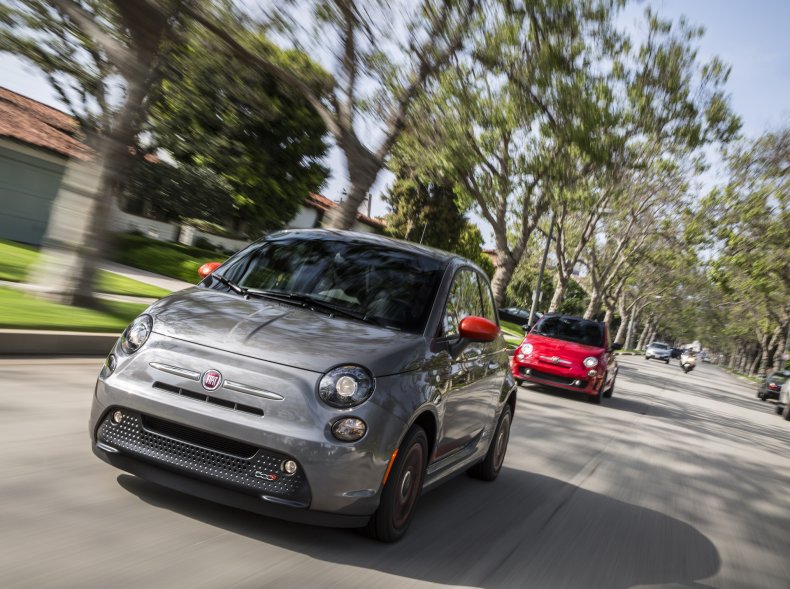
Fiat 500e

Stellantis
An electric version of the tiny hatchback was first put on display at the 2012 Los Angeles Auto Show. U.S. sales began in California in 2013 and Oregon in 2014.
A 24 kilowatt-hour liquid-cooled lithium-ion battery gave the car a range of 80 miles. The motor generated 111 horsepower and 147 pound-feet of torque.
Fiat announced that it was discontinuing its entire 500 line in the U.S. 2019.
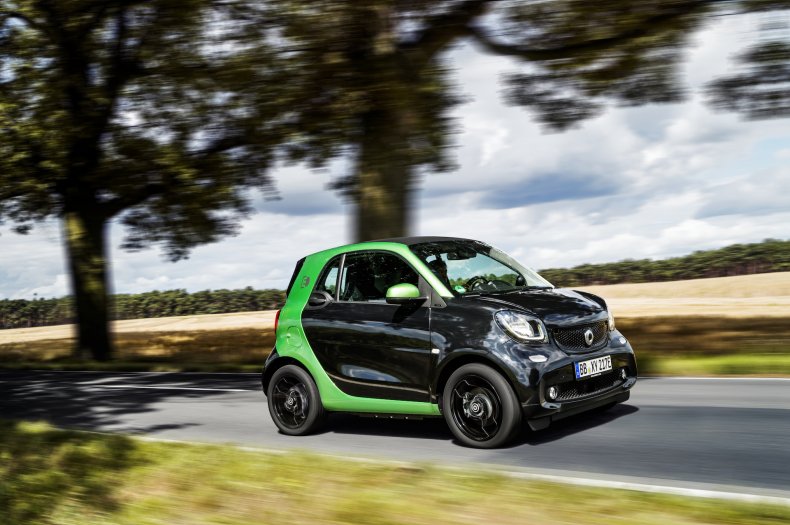
Smart Fortwo ED

Smart
On the road starting in 2007, the electric version of the microcar was introduced to the American market in 2011 with a trial run in major U.S. cities.
The first-generation 16.5 kilowatt-hour battery allowed for a range of 84 miles. The motor had an output of 27 horsepower and 89 pound-feet of torque.
Two years removing the gasoline-powered version from the U.S. market in 2017, Smart officially left the U.S. sales space.
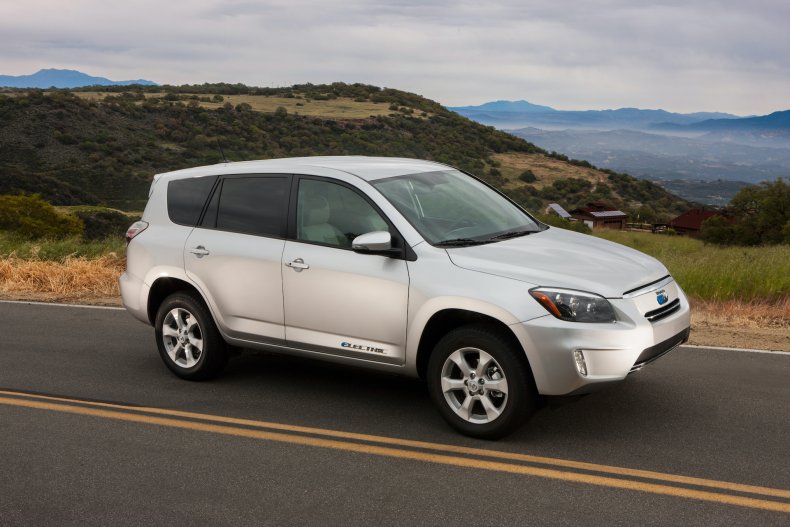
Toyota RAV4 EV

Toyota Motor Sales U.S.A. Inc.
A limited version of the first-generation RAV4 was made available to fleet customers in 1997. A nickel metal hydride battery gave it 95 miles of range. Synchronous permanent-magnet motors delivered 67 horsepower and 140 pound-feet of torque.
Toyota opened the RAV4 up to the public for sale in 2002 and sold 328 units, scrapping the car shortly afterward.
A second generation of the electric SUV began in 2012. The company sold around 3,700 of them from 2012 to 2014. This time around, a 41.8 lithium-ion battery powered the car, giving it a range of 103 miles. The motor produced 154 horsepower and 220 pound-feet of torque.



More Stories
Moon | Cartype
Rivian, Mercedes-Benz Joint Venture Paused
We Blew Up Our $5000 Drag Car ~ Can We Getting Fixed In Time? – Humble Mechanic